Fbi remotely installs spyware to trace bomb timer fbi remotely installs spyware to see text fbi remotely installs spyware to track fbi remotely installs spyware definition fbi remotely installs inc best fbi remotely installsure fbi remotely working

FBI remotely installs spyware to trace bomb threat
The FBI used a novel type of remotely installed spyware last month to investigate who was e-mailing bomb threats to a high school near Olympia, Wash.
Federal agents obtained a court order on June 12 to send spyware called CIPAV to a MySpace account suspected of being used by the bomb threat hoaxster. Once implanted, the software was designed to report back to the FBI with the Internet Protocol address of the suspect's computer, other information found on the PC and, notably, an ongoing log of the user's outbound connections.
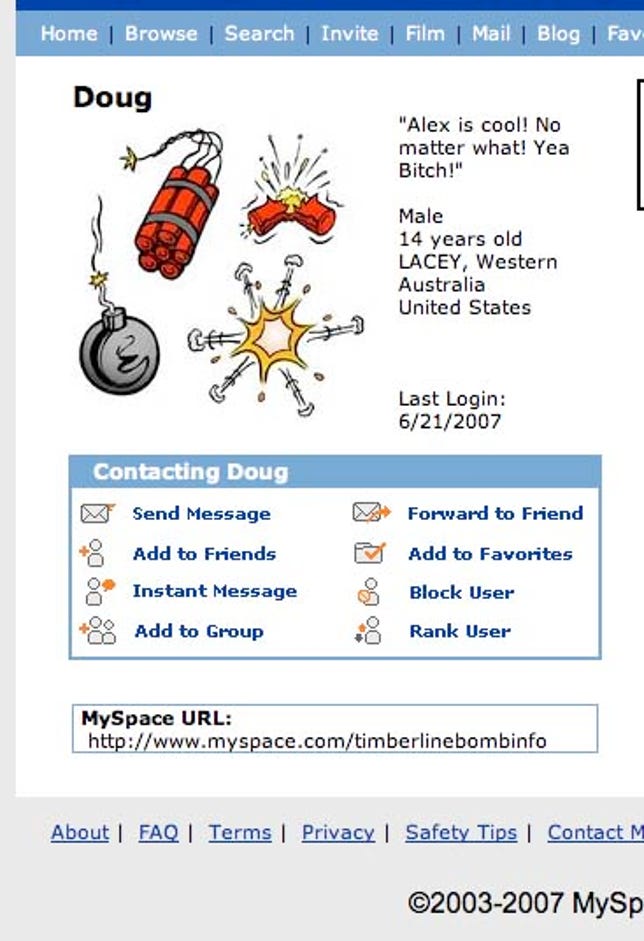
The suspect, a former Timberline High School student, was sentenced this week to 90 days in juvenile detention after pleading guilty to making bomb threats and other charges.
While there's been plenty of speculation about how the FBI might deliver spyware electronically, this case appears to be the first to reveal how the technique is used in practice. The FBI did confirm in 2001 that it was working on a virus called Magic Lantern but hasn't said much about it since. The two other cases in which federal investigators were known to have used spyware--the Scarfo and Forrester cases--involved agents actually sneaking into offices to implant key loggers.
An 18-page affidavit filed in federal court by FBI Agent Norm Sanders last month and obtained by CNET News.com claims details about the governmental spyware are confidential. The FBI calls its spyware a Computer and Internet Protocol Address Verifier, or CIPAV.
"The exact nature of these commands, processes, capabilities, and their configuration is classified as a law enforcement sensitive investigative technique, the disclosure of which would likely jeopardize other ongoing investigations and/or future use of the technique," Sanders wrote. A reference to the operating system's registry indicates that CIPAV can target, as you might expect given its market share, Microsoft Windows. Other data sent back to the FBI include the operating system type and serial number, the logged-in user name, and the Web URL that the computer was "previously connected to."
News.com has posted Sanders' affidavit and a summary of the CIPAV results that the FBI submitted to U.S. Magistrate Judge James Donohue.
There have been hints in the past that the FBI has employed this technique. In 2004, an article in the Minneapolis Star Tribune reported that the bureau had used an "Internet Protocol Address Verifier" that was sent to a suspect via e-mail.
But bloggers at the time dismissed it--in hindsight, perhaps erroneously--as the FBI merely using an embedded image in an HTML-formatted e-mail message, also known as a Web bug.
Finding out who's behind a MySpace account
An interesting twist in the current case is that the county sheriff's office learned about the MySpace profile -- timberlinebombinfo -- when the creator tried to persuade other students to link to it and at least one of their parents called the police. The sheriff's office reported that 33 students received a request to post the link to "timberlinebombinfo" on their own MySpace pages.
In addition, the bomb hoaxster was sending a series of taunting messages from Google Gmail accounts (including dougbrigs@gmail.com) the week of June 4. A representative excerpt: "There are 4 bombs planted throughout Timberline High School. One in the math hall, library hall, and one portable. The bombs will go off in 5 minute intervals at 9:15 am."
The FBI replied by obtaining account logs from Google and MySpace. Both pointed to the Internet Protocol address of 80.76.80.103, which turned out to be a compromised computer in Italy.
That's when the FBI decided to roll out the heavy artillery: CIPAV. "I have concluded that using a CIPAV on the target MySpace 'Timberlinebombinfo' account may assist the FBI to determine the identities of the individual(s) using the activating computer," Sanders' affidavit says.
CIPAV was going to be installed "through an electronic messaging program from an account controlled by the FBI," which probably means e-mail. (Either e-mail or instant messaging could be used to deliver an infected file with CIPAV hidden in it, but the wording of that portion of the affidavit makes e-mail more likely.)
After CIPAV is installed, the FBI said, it will immediately report back to the government the computer's Internet Protocol address, Ethernet MAC address, "other variables, and certain registry-type information." And then, for the next 60 days, it will record Internet Protocol addresses visited but not the contents of the communications.
Putting the legal issues aside for the moment, one key question remains a mystery: Assuming the FBI delivered the CIPAV spyware via e-mail, how did the the program bypass antispyware defenses and install itself as malicious software? (There's no mention of antivirus defenses in the court documents, true, but the bomb-hoaxster also performed a denial of service attack against the school district computers -- which, coupled with compromising the server in Italy, points to some modicum of technical knowledge.)
One possibility is that the FBI has persuaded security software makers to overlook CIPAV and not alert their users to its presence.
Another is that the FBI has found (or paid someone to uncover) unknown vulnerabilities in Windows or Windows-based security software that would permit CIPAV to be installed. From the FBI's perspective, this would be the most desirable: for one thing, it would also obviate the need to strong-arm dozens of different security vendors, some with headquarters in other countries, into whitelisting CIPAV.
Earlier this week, News.com surveyed 13 security vendors and all said it was their general policy to detect police spyware. Some, however, indicated they would obey a court order to ignore policeware, and neither McAfee nor Microsoft would say whether they had received such a court order.
The verbatim results of our survey are here.
Updated August 18, 2014: The name of the Timberline High School student, who was a minor at the time of the incident, has been removed.
Source

